StatPlus for Mac: statistics software review (version 5.3.5.1 — current version is 5.4)
It seems that every time we review StatPlus for Mac, the publisher addresses all of our concerns and issues a new release a few days later. The rest of this review discusses version 5.3.5.1, but the current version is 5.4, and it has numerous changes. The most important are:
- You no longer have to switch in and out of Excel; you now have an Excel add-in which provides the StatPlus menus within the program. That saves an incredible amount of time.
- Missing values and alphanumerics are, we are told, handled far better than in the past.
We fully expect that by the time we review 5.4 and update this page, a version 5.5 with a syntax language and nicer output options will have appeared. That said, watch this space and we’ll try to get up to date before AnalystSoft figures out what we want and gives it to us.
StatPlus is based on a Windows program, but AnalystSoft reprogrammed it completely in Applescript, optimized for either Intel or PPC (which means it takes advantage of the G4 and G5’s math capabilities). Because of this, it is fast and has none of the usual quirks of Windows ports.
The basic idea is quite clever, because the key weakness of many statistical packages is their spreadsheet-style data view, which is usually missing, clunky, or very clunky. Many people end up using Excel, Numbers, or OpenOffice to prepare their data and make simple tables, and then go into serious statistical machines to run analyses. In the end, many copy tables out of SPSS or R or Stata and paste them into Excel. SPSS 17 even has a moderately clunky "Excel export mode."
Why not just use Excel to hold the data and the findings? StatPlus does just that.
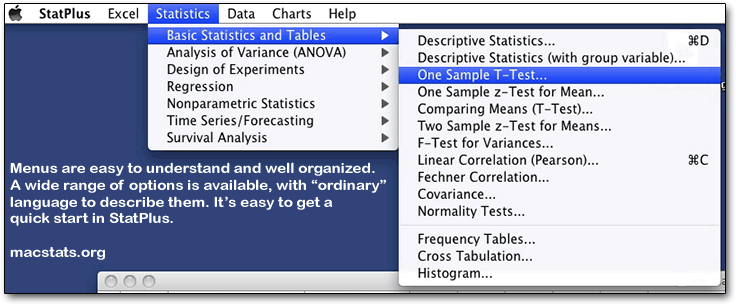
StatPlus itself is a fairly small, fast-loading program that has a small number of menus — one that launches Excel; one that provides statistical analyses; and one that manipulates data. The analyses menu provides simple, easily understood categories, and underneath those are submenus with the actual operations. It’s easy to learn, yet contains numerous statistical methods that are not normally provided by easy-to-learn software, including one, two, and three way ANOVAs, GLM models, and many other analyses. The Help system is fully developed, in a standard Mac format, and is moderately easy to read. Cleverly, StatPlus launches Excel automatically when you start it up, saving a step and making it seem more seamless.
You can also prepare your data with tools above and beyond those provided by Excel:
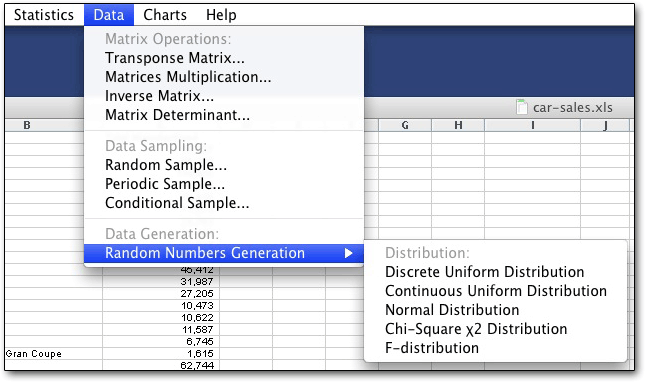
One item of interest is how much more you get with version 5 of StatPlus than with version 4. One nice thing about not having to play around with the user interface all day is that the programmers can keep building in new capabilities.
Once you select a procedure, you get a dialogue box asking you to select a range in Excel (or, in the case of frequency tables, a question asking if you have discrete or continuous variables. StatPlus has one advantage over SPSS there — you won’t get a never-ending printout of nearly identical frequencies.)
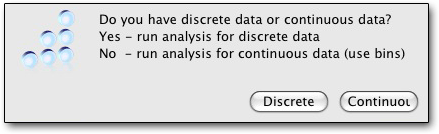
If you've already selected a range, just click Range; you will be put into Excel, but you can just come back to StatPlus. If you haven't already selected the range of data you want, the program will still put you into Excel, where you can select what you want and then return by clicking on StatPlus in the dock or cloverleaf-tabbing back.
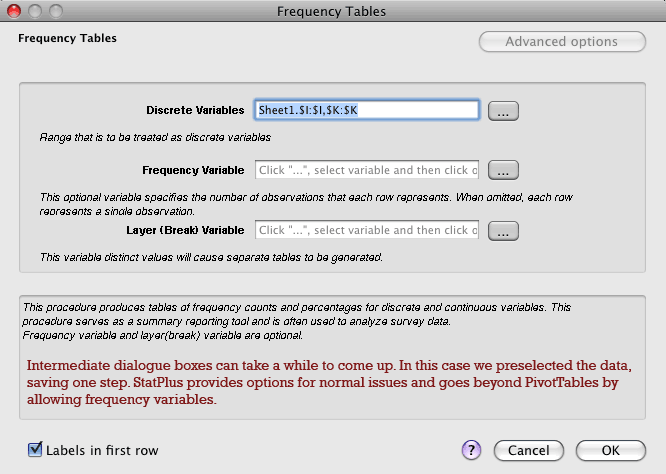
It may take a few seconds (longer on slower machines; we tested on a Macbook Pro and a Mac Pro), but you will get an intermediate box like the one above (for frequency tables). Advanced options is often grayed out, but when you can use it, it provides more control in some cases. Go on, try this in SPSS:
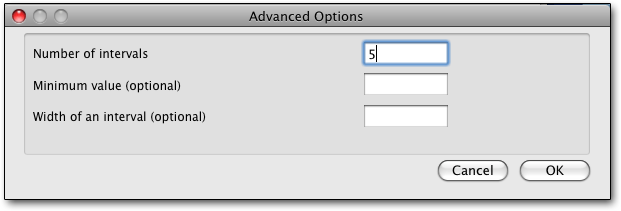
Once you click on OK, it can take anywhere from the blink of an eye to around ten seconds for a moderately sized data set to get analyzed, with no feedback at all. Then Excel opens up, a new worksheet is created, and the program writes out its tables to Excel.
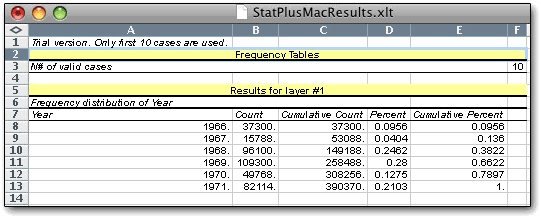
One new problem we encountered is that the program demands you save or copy out the results of the prior analysis before going into another one, or else it will simply overwrite whatever you have. Since there's no syntax or logging going on, that can mean a fair amount of work to re-create existing work. Fortunately you do get an error message, but it's strange that it can't just open up a new tab, or go down to the first blank cell. Oh, and you can't change the default formatting of the tables you get - so those of us with poor vision will just have to deal with 10-point Arial.
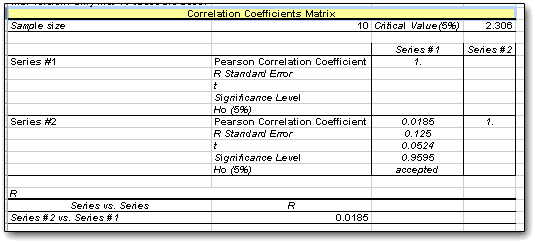
The reason this layout looks a little funny is that the system only prints out the area underneath the line, which makes large correlations more readable. Unfortunately, it also prints out everything you see above, whether you want it or not; there's no abbreviated version with just the R and an asterisk to show if it’s significant at a particular level. In the example shown above, incidentally, we used random numbers generated by StatPlus.
Regressions include the R, R-square, adjusted R-square, and the weighting of coefficients with the intercept. A surprising number of regression types are allowed, but options are limited — for best subsets, the minimum probability to enter; for linear, residual and line fit plots can be added. (Best Subsets is also known as stepwise regression; simultaneous regression tests all variables as independent and dependent.)
Starting in version 5, StatPlus easily deals with empty cells acceptably. However, it still can’t deal with alphanumerics in frequency tables, giving us a strange message about invalid float.
When StatPlus does work, it can be impressive, if slow with larger datasets:
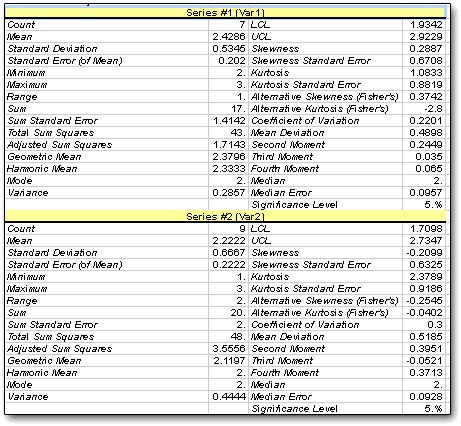
The general usage of StatPlus can be awkward, with a lot of switching between the program and Excel, and no indication of when the program is working, with delays between selecting a process or a range and getting some sort of reaction. The addition of keyboard commands for descriptive stastistics and correlations helps, but more processes should be keyboard-accessible; and it would be good if there was a way to keep the program with Excel, to add to the output, to use variable labels, and to use alphanumeric data in frequency counts (especially since there is no support for variable labels, so if you convert alpha to numeric, you have to write down how you did it).
StatPlus can be a handy tool for the statistical dabbler or Excel maven who uses Excel to prepare both their data and their output, but its cost rivals that of numerous other programs that keep everything self-contained, and the easy menu layout and options choices are countered somewhat by the need to learn exactly how to make StatPlus happy.
Sponsored by Toolpack Consulting • Related Videos
Copyright © 2005-2025 Zatz LLC. All rights reserved. Created in 1996 by Dr. Joel West; maintained since 2005 by Dr. David Zatz. Contact us. Terms/Privacy. Books by the MacStats maintainer

